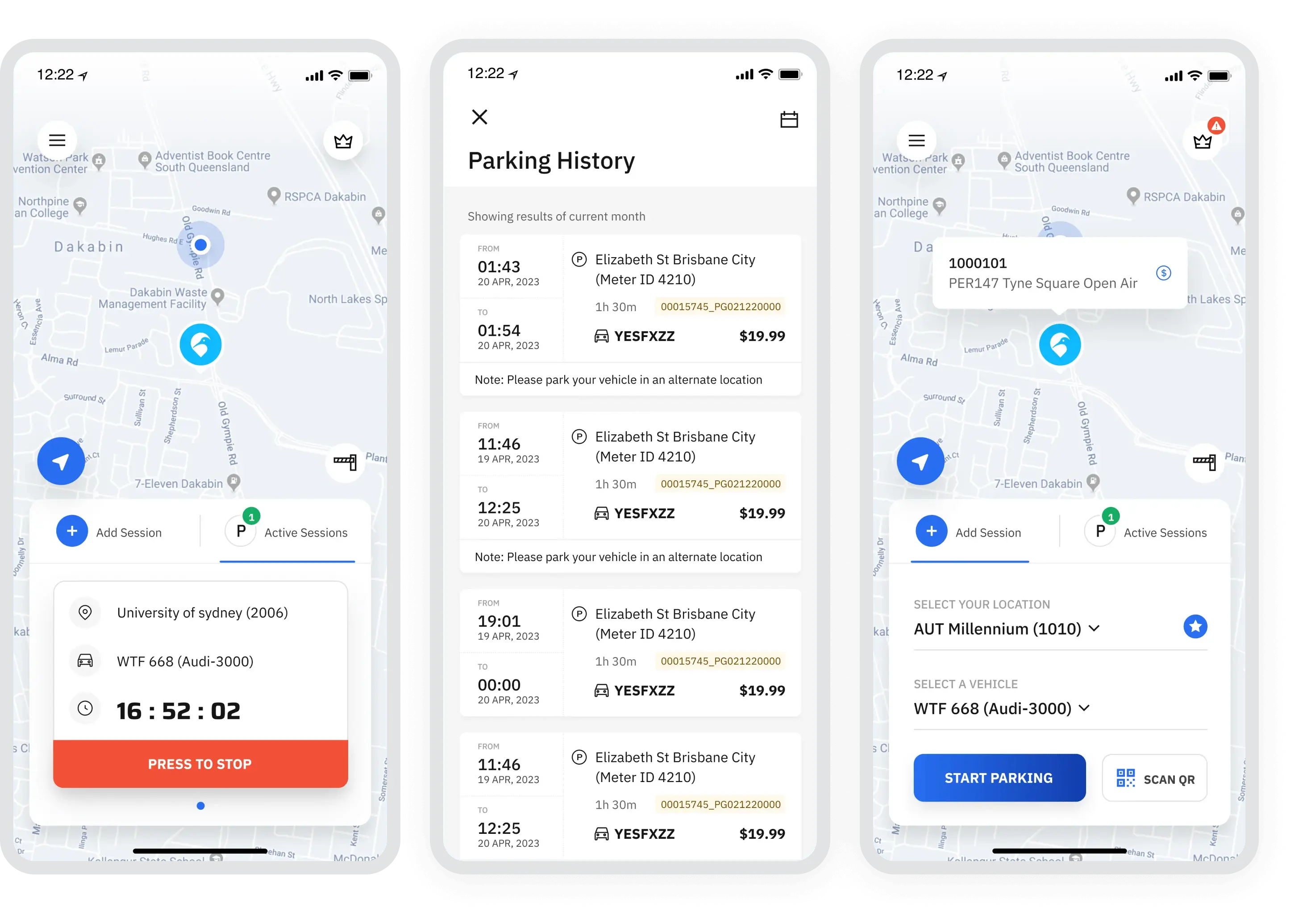
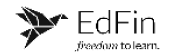ParKiwi is a mobile-first parking app that helps users easily pay and manage parking across Australia, New Zealand, and the US. With a seamless design, AI, and location services, it delivers a modern and accessible parking experience. Here’s what we achieved with ParKiwi:
- State-of-the-art user experience
- Zero-knowledge onboarding
- Geolocation and Bluetooth-based auto parking start/stop
- End-to-end integration for seamless drive-in, drive-out parking
- Continuous innovation enabling growth across 3 nations